For the past years, PERC solar cell technology has been one of the R&D favorites in the PV industry.
PERC stands for Passivated Emitter Rear Contact and refers to the dielectric layer on the back of a PERC solar cell.
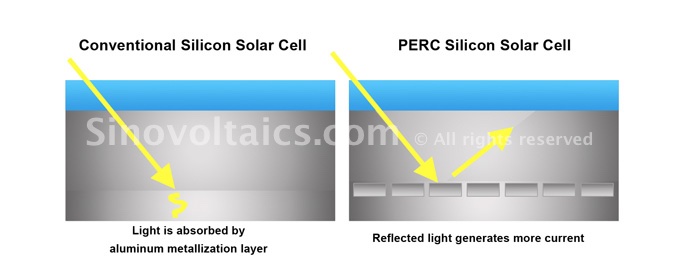
This layer on the back of the solar cell helps to reflect light, that passed through the cell, back into the cell so it can generate more electrons. This is also known as backside passivation.
PERC: both efficiency increase and cost reduction?
When it comes to R&D, there are two obvious focus points in our industry: cost reduction and efficiency increase.
With efficiencies passing the 20%+ mark, PERC solar cell technology surely has an advantage compared to conventional P-type Si solar cells, which only produce around 18-19%.
The efficiency gains of PERC technology translates into a 3-5W power increase for a 60 cell mono module.
Besides higher efficiency, PERC solar cell technology will potentially have a cost advantage as well. However, this requires that sufficient PERC manufacturing capacity has been installed and production has been ramped up.
And yes.. the factories in Asia have been ramping up their PERC capacity.
Why will PERC be the dominating solar cell technology?
As PERC is compatible with existing screen printing equipment, it’s fairly easy for manufacturers to upgrade their existing production lines.
A lot of Asian manufacturers, such as JA Solar, Trina Solar, NeoSolar, Gintech, Hanwha Q Cells, and Suntech, have already upgraded their production lines, and several others are in the process of doing so.
Moreover, prominent PV production machinery suppliers such as Meyer Burger and Centrotherm are involved in the manufacturing of PERC cell production equipment.
What are the main Asian manufacturers with PERC solar cell technology?
Solarworld announced in July 2015 that it currently owns the largest PERC cell production capacity in the world. Its current cell manufacturing capacity reached 800MW.
For a company like Solarworld, it kind of makes sense to expand on their high efficiency production lines, as they mainly focus on the High ASP (average selling price) markets.
Industry insiders do realize that it won’t be long before the lower cost, Asian manufacturers will catch up and surpass this capacity.
In fact, at the time of writing we see the major Chinese manufacturers expanding PERC capacity fast:
JA Solar – PERCIUM solar cells
The expected production capacity of JA Solar’s PERCIUM solar cells is 350MW in 2015, which is only a small part of its total expected 3.6-4.0 GW sales capacity (PV-Tech).
The company has reached average conversions efficiency of 20.4%. JA Solar started marketing its PERCIUM 60 cell solar panels already in 2014 in mainly the Japanese, British, Israeli, Chinese, and German markets.
Suntech – HYPRO Solar Cells
Good to see that Shunfeng, the owner of the Suntech brand, is also investing in upgraded production lines at Suntech and has been implementing PERC solar cell technology.
The first Hypro module production line came online in July 2015 and Suntech has started shipping out high efficiency modules for its first projects.
Suntech’s 60cell, 290W modules reach a max. of 20.5% conversion efficiency, and it's 72 cell Hydro module produces 345W.
Trina Solar – Honey M Plus
In early 2015, Trina Solar launched both a poly and mony PERC solar module, called Honey Plus. The mono module is called Honey M Plus.
The Poly Honey Plus reached an efficiency of 18.7%, 60cell reaches 275W, while the Honey M Plus has a conversion efficiency of 20.4%, which makes a 60cell module 285W (Trina).
Trina Solar states that it offers the Honey Plus PERC solar cells with five-busbar frontside contacts, which slightly lowers the resistance and increases reliability.
Why would a 5 busbar solar cell be more reliable? The main reason is that it reduce the effect of inactive parts of a solar cell in case of micro cracks.
Jinko Solar – Eagle+ modules
In May 2015, Jinko Solar opened a new PERC cell and module manufacturing facility in Penang, Malaysia. The solar cell capacity was announced to be 500MW and the PV module capacity 450MW (Jinko Solar).
Jinko recently announced that it manufactured a high efficiency 60cell, 306.9W module in its lab, however, regular manufacturing efficiencies seem way below this output.
How does PERC cell technology improve solar panel performance?
As explained already, PERC solar cells are designed with an additional layer at the bottom of the solar cell. This extra layer is called the dielectric passivation layer.
There are three main reasons why the dielectric passivation layer contributes to the increase of efficiency:
- The extra dielectric passivation layer reduces electron recombination:
Electron recombination is the tendency of electrons to recombine and basically block the electrons from freely flowing through the solar cell, which means it can’t reach its potential efficiency. Electrons generated near the back of the solar cell are now free to move up to the emitter and contribute to more electrical current. - The extra dielectric passivation layer increases the solar cell’s ability to capture light:
The dielectric layer reflects the light that passes through the solar cell without generating any electrons. By reflecting this light, the photons are given more opportunities to generate electrical current. - The extra dielectric passivation layer reflects wavelengths above 1180 nm out of the solar cell, which would normally create heat:
Silicon wafers stop absorbing wavelengths above 1180 nm. In normal solar cells, such wavelengths are easily absorbed by the backside metallization and turned into heat.As you know, heat reduces the solar cell’s conversion efficiency. The dielectric passivation layer reflects wavelengths above 1180 nm out of the solar cell and helps the solar cell to work more efficiently by maintaining cooler temperatures.
Review: How is electricity generated from a solar cell?
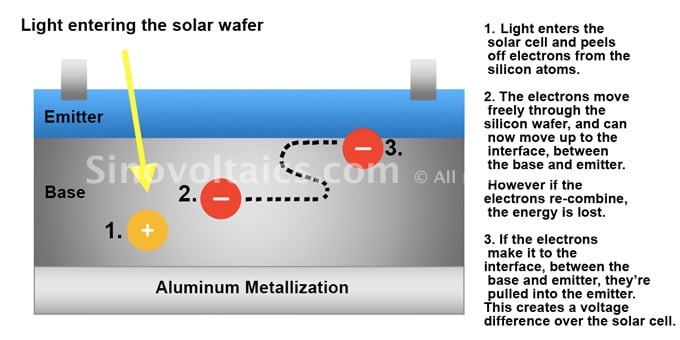
Conventional crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cell consists of two layers with different electrical properties. The two layers are called the base and the emitter. The point where the base and emitter meet is called the interface.
An electrical field is generated where the two layers touch – this point is called the interface. The interface pulls negatively charged electrons into the emitter once reaching the interface.
When light enters the solar cell, the electrons are released from the silicon atoms.
When electrons are released, they can travel freely through the silicon wafer. However, the electrons will only contribute to the electrical current if they reach the interface, between the emitter and the base.
Once electrons reach the interface, they’re pulled into the emitter and will create a voltage difference over the solar cell.
Different types of wavelengths
Shorter wavelengths (blue light) mainly generate electrons near the front of the solar cell, while the longer wavelengths (red light), will generate electrons at the back of the cell. Some of the longer wavelengths will pass through the wafer without generating any current.
This is where the dielectric layer on the back of the solar cell makes the difference.
How PERC cell technology catches different wavelengths
The sun emits light in different wavelengths and when the light reaches the silicon cell structure, it generates electrons at various levels of the solar cell structure.
PERC technology increases the cell’s ability to catch longer wavelengths. The longer wavelengths are especially present during mornings and evenings (sun under an angle) or during cloudy days.
Blue light, with shorter wavelengths, is being absorbed by the atmosphere during these times, as it has to travel a longer path to reach the Earth’s surface. Red light is less easily absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere.
So the main reason why PERC technology shows better energy yields is the reflective dielectric layer on the back of the solar cells which helps to absorb more red light, even during the morning, evenings, or during cloudy weather.
TO OUR READERS:
Are you engaged in the manufacturing, importing or installation of PERC cell modules or do you own a PV system using PERC cells? What has been your experience so far in terms of in-field performance? Please comment!








OM Nangia
on 11 Mar 2016