While it’s been a while since we’ve seen a large Asian solar PV module manufacturer file for bankruptcy, the past years have taught us to always keep a close eye on the financials of the large Asian manufacturers. One quick method to evaluate the financial shape of a PV manufacturer is to use the Altman Z-Score, which we’ll explain in this article.
Most recently we saw Taiwanese CIGS manufacturer TSMC close its doors in 2015, while we all clearly remember both Suntech and LDK file for bankruptcy in 2014, not to mention many more small- and medium-sized manufacturers all over the continent.
So which PV manufacturer is next?
Already last year it was widely known that the former largest (2012/2013) PV manufacturer Yingli was in financial trouble. The company hasn’t reported a profit since 2011 and has been accumulating short and long-term debts ever since.
As a PV plant developer, installer, or distributor that fully relies on the supply of its modules from an Asian manufacturer and in this regard also the related warranty policies, how to assess the risk of your manufacturing partner going bankrupt, without devoting a complete study on its financial reports?
How to quickly see which PV manufacturer may be in financial distress?
One proven and fairly quick way to predict if a PV manufacturer may face bankruptcy within the next 2 years is the Altman Z-Score.
What is the Altman Z-score?
The Altman Z-score is a formula to predict bankruptcy. This formula is used to predict corporate defaults and the status of financial distress. The formula can be used to predict the probability that a firm will go into bankruptcy within two years.
As the Altman Z-score was originally designed to assess public manufacturing companies with assets of more than USD 1 million, this formula is an excellent way to assess which PV manufacturers may be in trouble within the next 2 years.
The formula is nowadays widely accepted by auditors, accountants, courts, and database systems used to evaluate loans.
The formula dates from the 1960’s and was published by Edward L. Altman, who back then was working as an Assistant Professor of Finance at New York University.

Altman Z-score: how likely is a PV manufacturer to go bankrupt within the next 2 years?
How reliable is the Altman Z-score formula?
We’d say reliable enough to make a proper judgment on the financial situation of a PV manufacturer:
Between 1968 and 1999 the formula has been put to the test multiple times. The model was found to be about 80-90% accurate in predicting bankruptcy one year before the event (with a Type II error (classifying the firm as bankrupt when it does not go bankrupt of approximately 15%–20%*).
(*Source: pages.stern.nyu.edu/~ealtman/Zscores.pdf)
How’s the Altman Z-score calculated?
Altman Z-Score = 1.2A + 1.4B + 3.3C + 0.6D + 1.0E
The original formula is broken down as following:
A = Working Capital/Total Assets: measures liquid assets in relation to the size of the company.
B = Retained Earnings/Total Assets: measures profitability that reflects the company’s age and earning power
C = Earnings Before Interest & Tax/Total Assets: measures operating efficiency apart from tax and leveraging factors. It recognizes operating earnings as being important to long-term viability.
D = Market Value of Equity/Total Liabilities: adds a market dimension that can show up security price fluctuation as a possible red flag
E = Sales/Total Assets: a standard measure for total asset turnover)
How is the Altman Z-scores interpreted?
The scores are categorized into 3 zones called the Safe Zone, Grey Zone and Distress Zone:
Z > 2.6 -“Safe” Zone
1.1
Z
How do Asian PV manufacturers rate on the Altman Z-score?
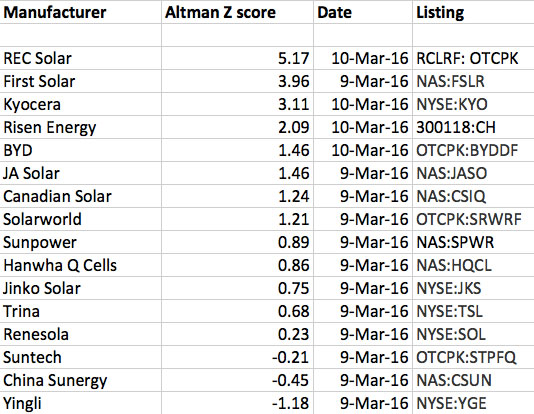
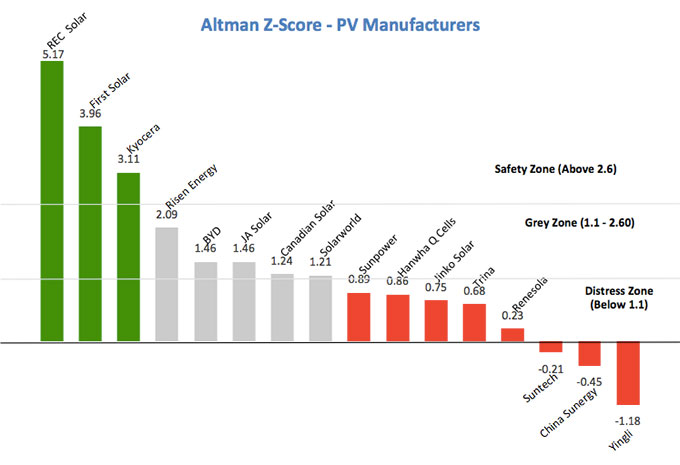
A lookup on Gurufocus returned the following results:
Altman Z-Score – PV manufacturers
Altman Z-Score – PV manufacturers
Source: www.gurufocus.com
As a comparison between Asian and Western PV manufacturers, we’ve included the Altman Z-scores of the major European and American manufacturers such as Solarworld, First Solar, and Sunpower. With a score of 3.96, First Solar is comfortably in the Safety Zone, while Sunpower is in much worse shape, together with Hanwha Q Cells and Jinko Solar at the top of the Distress Zone.
Earlier news about Yingli Solar struggling with its debts is here confirmed. The company rates at the very bottom with -1.18 on the Altman Z-score, which means it’s in the Distress Zone and is likely to face bankruptcy within the next 2 years. Also, China Sunergy, Suntech, and Renesola are in the bottom part of the Distress Zone.
Interestingly, manufacturer Risen Energy is, amongst the Chinese PV manufacturers, in the best financial shape and leads at the top of the Grey Zone with a score of 2.09, leaving behind BYD, JA Solar, and Canadian Solar. This shows us that the large, known brands are not necessarily the financially most stable companies.
Altman Z-Score and limiting real-world factors
While the Altman Z-Score is quite reliable to make proper judgments on the financial shape of a PV manufacturer, there are of course many more local factors that can come into play in the wake or aftermath of a bankruptcy of a manufacturer.
Such factors can be the strategic importance of a manufacturer, the number of people employed, unique technologies or intellectual properties, shareholder interests, and so on.
In the case of China for example: as these Chinese companies at the bottom of the distress zone are large employers in China with significant manufacturing investments, even if they would have to file for bankruptcy, support from the government to keep them alive would however not be an unlikely scenario.
Do you want access to Altman Z-Scores of all leading PV module manufacturers? Access Full Version: Altman-Z Report with 60+ PV module manufacturers for FREE.






Antos
on 09 Nov 2016matt
on 28 Apr 2016Dricus
on 20 May 2016