Smart MicroGrids
Introduction to Microgrids
Traditionally, most countries have been relying on centralized grids to fulfill their electricity needs. However, recent times have seen the emergence of ‘smaller’ and ‘independent’ grids that are meeting energy needs of small communities locally and devoid of any dependence on central grid. Such grids called as Smart Microgrids are free standing grids. While they can be made to operate in tandem with central grids, they are mostly designed to cater to energy needs of local population and run autonomously as self-sufficient power units. As an example, they can be set up to meet the electrical demand of a single costumer or of various customers in university campus, offices, or of a village community in rural area. They are comprised of small-interconnected clusters of loads that aim to provide reliable and ‘grid’ free power in a cost effective manner. The Microgrid components are: Distributed energy resources (DERs) such as PV or wind energy, storage devices such as batteries, and finally the loads. Smart Microgrids are a newer technology and an extension to the regular Microgrids. They use software and intelligent controls to manage electricity flow in networks. 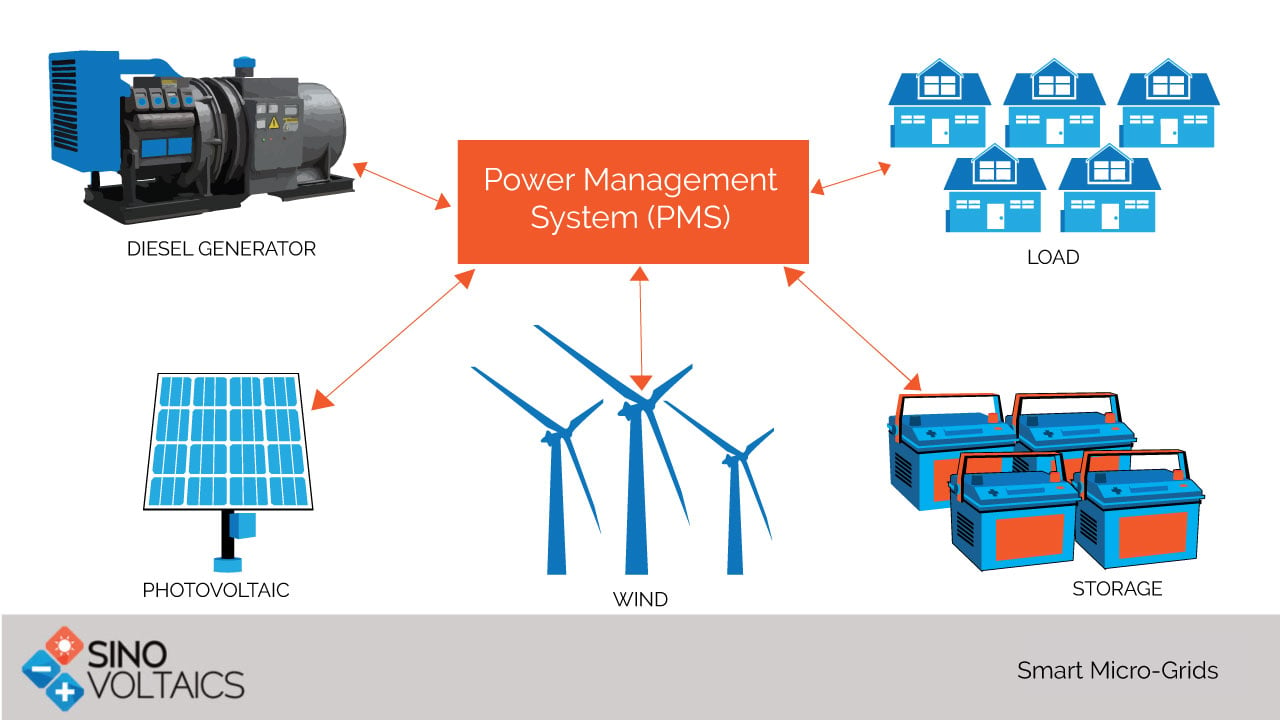
Smart Microgrids –Main features
Smart Microgrids use: 1) Digital information and control 2) Real time efforts to optimize the grid operations 3) Smart metering system, smart real time integration (real-time response information on energy consumption) and an electricity storage. Moreover, smart grids have other advantages such as being robust; can use distributed energy resources and provide higher power quality and higher capacity factor.
Types of Technologies used in Smart Microgrid
Ø Smart switches, relays and sensors that meet power needs more efficiently and reliably. Ø The infrastructure is quite well protected, normally installed underground Ø Computerized real time controls that can anticipate potential instabilities to correct problems before users experience any disruption in energy service.
Benefits of Smart Microgrid
- Improvement over traditional Grid: At the local level, Smart Microgrids are efficient way to easily and cost effectively integrate consumers and networks with electricity distribution and generation.
- Greater Reliability — Local power generation is a great way to eliminate blackouts. Technologies such as smart switches and sensors can anticipate and fix power disturbances, compared to manual switches in traditional grids used to handle an outage.
- Cost Effective: Microgrids allow consumers to obtain electricity in real-time at lower costs, as it relies on locally generated power thus avoiding peak electricity that is costly. The Microgrid model also shields from infrastructure improvement costs that are common in traditional grid model and which are borne by the ratepayers.
- Encourages local employment — Small communities with Microgrid models can result in job creation at the local level.
- A Methodology for future-proof Grid — A big plus of Smart Microgrids is that they are much better positioned than the centralized grid to meet the electricity needs of the future. Local communities can reliably depend on them to meet their energy needs quickly and efficiently through small local generators, solar cells, wind turbines etc. Conventional grids are costly to extend up to local remote areas and take many years to come online.
- Reduces Carbon footprint — Smart Microgrids are equipped to use waste heat from their locally generated electricity. For example they can reuse the energy that is produced during electricity generation for heating buildings or hot water and for cooling and refrigeration purpose too.
