Base Load and Peak Load: understanding both concepts
What are Base Load and Peak Load?
Load, in electrical engineering, is the amount of current being drawn by all the components (appliances, motors, machines, etc.). Load is further categorised as base load and peak load depending upon the nature of the electrical components connected. As you may be familiar, all electrical appliances at your home do not run at all times.
- A toaster or microwave oven may be used for a few minutes,
- A television or computer may be used for a few hours
- Lighting in the house is only required during the evening and so on.
There are several appliances which keep running at all the times, no matter what. The refrigerator, for example, has to be plugged in at all the times. Another such example are the heating, ventilation and cooling systems in the house (HVAC system).
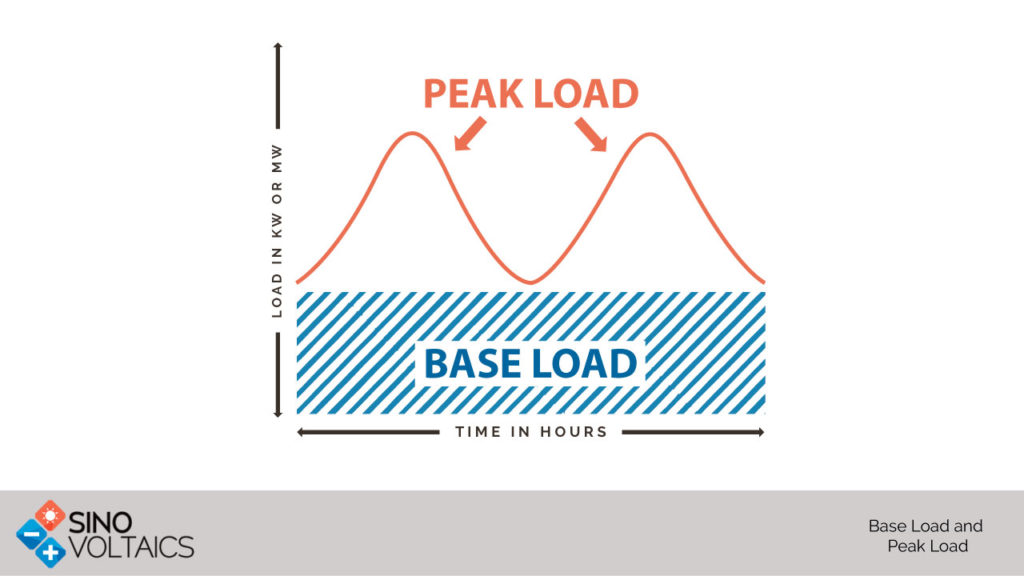
Peak Load and Base Load defined
Base load is the minimum level of electricity demand required over a period of 24 hours. It is needed to provide power to components that keep running at all times (also referred as continuous load). Peak load is the time of high demand. These peaking demands are often for only shorter durations. In mathematical terms, peak demand could be understood as the difference between the base demand and the highest demand. Now going back to the examples of household loads: microwave oven, toaster and television are examples of peak demand, whereas refrigerator and HVAC systems are examples of base demand.
A broader perspective of understanding these concepts
Now on a broader perspective, it could be assumed that the electrical grid is a big household. Under normal circumstances, the power required by the electrical grid is fairly constant during various period of the day. This constant power, which is required at all times, is called the base loading. But during a special event, like the final match of World Cup, the demand will be more, as a lot of people will watch TV. This short, high demand period is considered to be a peak loading. Base Load and Peak Load
Base Load and Peak Load power plants
Power plants are also categorised as base load and peak load power plants.
Base Load Power plants
Plants that are running continuously over extended periods of time are said to be base load power plant. The power from these plants is used to cater the base demand of the grid. A power plant may run as a base load power plant due to various factors (long starting time requirement, fuel requirements, etc.). Examples of base load power plants are:
- Nuclear power plant
- Coal power plant
- Hydroelectric plant
- Geothermal plant
- Biogas plant
- Biomass plant
- Solar thermal with storage
- Ocean thermal energy conversion
Peak Load Power plants
To cater the demand peaks, peak load power plants are used. They are started up whenever there is a spike in demand and stopped when the demand recedes. Examples of gas load power plants are:
- Gas plant
- Solar power plants
- Wind turbines
- Diesel generators
Looking to enhance the efficiency and reliability of your solar energy systems? Contact us to learn how we can help you improve system performance and secure the long-term success of your solar projects.

Bikash sharma
on 18 Sep 2022Sylvester Kemei
on 29 Apr 2016Jain k b
on 22 Jan 2017Sarojkumar
on 09 Feb 2018Austin
on 09 May 2016James
on 22 May 2016madhu
on 07 Jun 2016sylvester Ossai
on 27 Jun 2016Elisha Akobueze .U
on 07 Jul 2016sivaprakasam
on 13 Jul 2016Fagbemi Ademola
on 18 Jul 2016Aziaka D.S
on 19 Jul 2016Ashish
on 27 Nov 2016bhagwat
on 28 Dec 2016M rashid
on 04 Jan 2017Manoj Arora
on 05 Jan 2017SAYAK PAL
on 19 Feb 2017Sunday Baduku
on 08 Sep 2017Sahibzada Abdul Haseeb
on 11 Oct 2017Peter
on 28 Nov 2017Vishal
on 09 Feb 2018Khairul
on 08 Apr 2018Dr. Ramana
on 13 Apr 2018Soumyarup chowdhury
on 26 Apr 2018Govt ITI HIRAKUD
on 05 Sep 2018Kekeli
on 12 Sep 2018Rahul Panchal
on 07 Mar 2020