- Electromagnetic Nature of Solar Radiation
- Insolation vs irradiance
- The Source of Never-Ending Energy
- Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI)
- The Journey from the Sun's Core to the Earth's Surface
- The Inverse Square Law
- Components of Solar Radiation
- Factors Affecting Solar Insolation
- Solar Insolation Explained
- Solar Insolation Maps
- Global Solar Potential
Difference Solar Radiation and Solar Insolation explained
Understanding the electromagnetic nature of solar radiation and solar insolation is crucial for harnessing solar energy to generate electricity. This article delves into the physics of solar radiation, the journey of solar energy from the sun to the earth, and the factors affecting solar insolation.
Electromagnetic Nature of Solar Radiation
Definition of solar radiation: Solar radiation is the radiant energy emitted from the sun, encompassing the complete frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, and near-visible radiation (UV Rays, Infrared Rays, X-rays, etc.). This solar radiation, together with other factors, supports life on Earth, while the Earth's atmosphere deflects harmful near-visible radiation.
Insolation vs irradiance
What is insolation? Insolation definition: Insolation is the measure of solar radiation energy received on a given surface area in a given time, typically expressed in watts per square meter.
Solar irradiance definition: Solar irradiance is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument, usually expressed in watts per square meter.
Thus, solar irradiance measurement is an instantaneous measurement, whereas solar insolation is a cumulative measurement over time.
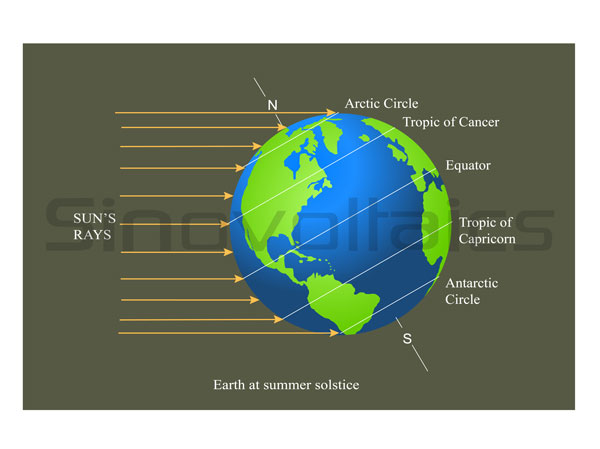 Earth at summer solstice
Earth at summer solstice
The Source of Never-Ending Energy
The sun has a power output (luminosity) of about 3.9 x 1026 Joules per second, generating its energy through a nuclear fusion reaction that converts approximately 700 million tons of hydrogen to helium every second process creates massive amounts of heat, causing photons to be emitted. These photons travel a short distance before being absorbed by other molecules, which then emit another photon. This absorption and re-emission process continues until the photons reach the sun's surface and are radiated into outer space.
Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI)
Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI) refers to the amount of solar radiation received per unit area by a surface perpendicular to the incoming solar rays. To maximize the energy production from a photovoltaic (PV) module, it is essential to track the sun's movement and ideally keep the PV module perpendicular to the incoming solar rays, which can for example be achieved with solar trackers.
 Direct Normal Irradiance
Direct Normal Irradiance
The Journey from the Sun's Core to the Earth's Surface
The journey of solar radiation from the sun's core to the sun's surface typically takes around 100,000 years. Once in outer space, the photon is radiated and intercepted by other celestial bodies such as planets as light. The journey from the sun's surface to the earth's surface takes approximately eight minutes.
The Inverse Square Law
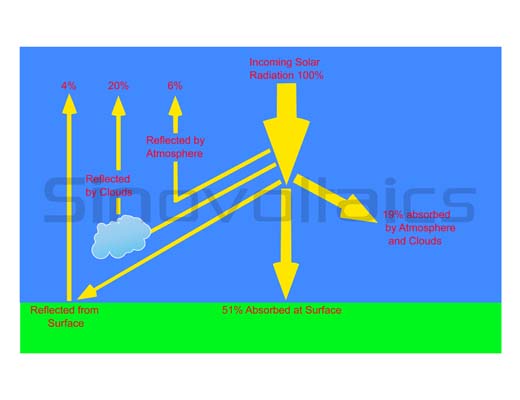
The total energy emitted by the sun is 63.000.000 W/sq. m. The intensity of solar radiation striking the earth is determined by the Inverse Square Law. This law states that the total radiant energy striking the earth's surface is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Only about 40% of the solar energy intercepted by the earth passes through the atmosphere and is available for solar applications.
Components of Solar Radiation
Solar radiation is composed of three components:
- Direct Radiation: The radiation that comes directly from the sun.
- Diffused Radiation: The radiation diffused by the sky, layers of the atmosphere, and other surroundings.
- Reflected Radiation: The radiation reflected back by water bodies, such as lakes and seas.
The total ground reflection is the sum of all three components.
Factors Affecting Solar Insolation
Solar insolation, or the amount of solar radiation received on a surface over a period of time, is influenced by various factors, including:
- Atmospheric Conditions: The presence of cloud cover, the condition of the ozone layer, etc.
- Earth's Rotation: The time of the day, solar activity, etc.
- Earth's Revolution: The distance between the Earth and the sun, seasons, angle of inclination of the Earth's surface, etc.
Solar Insolation Explained
Solar insolation refers to the quantity of solar radiation energy received on a surface of size X m² during an amount of time T. In the photovoltaic industry, it is commonly expressed as average irradiance in kilowatt per square meter (kW/ m²) or - taking into account the time factor - kilowatt hours per year per kilowatt peak kWh/(kWp*year).
Solar Insolation Maps
Solar insolation maps display the average daily hours of solar insolation in a specific area. These maps help solar system designers determine the size of solar systems and estimate their output by considering the insolation of a particular area.
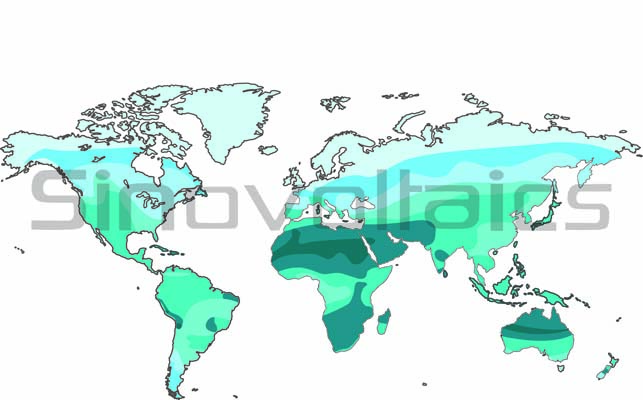
Global Solar Potential
The Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) upon the earth is approximately 1.361 kW/ m², with a theoretical potential of 694.11 terawatts on the earth's surface area of about 510 million square kilometers. The southern hemisphere and desert areas have a large potential for solar-generated electricity.
Interested in understanding how your project location compares in solar potential — or how to maximize performance under local irradiance conditions? Let’s talk. Our solar engineering team can analyze your site’s data and guide you toward the most effective system design.

Abdulrasheed Lukmon
on 16 Jul 2021p.uma maheshwar rao
on 10 May 2016Chukwuemeka Okezie
on 20 Oct 2016H.T.Abdulkarim
on 14 Sep 2017aditya mishra
on 03 Nov 2017chavah s.
on 23 Apr 2018Brett
on 24 Sep 2018Laurence wentzel
on 31 Jan 2019kintoh Priscilla
on 26 Jan 2020