Compressed Air Energy Storage
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Overview
CAES is one of the commercial utility scale grid storage technologies where aim is to store energy during periods of low energy demand and extract it for use later during periods of high-energy demand. Furthermore, CAES technique involves storing a stream of air as compressed gas. To achieve this, ambient air is being pumped into big storage tanks or in caverns located underground or deep underwater. This is done using valve mechanism using some external source of energy (like natural gas) so that the forced air is pushed inside the tanks but cannot exit it from the same passage 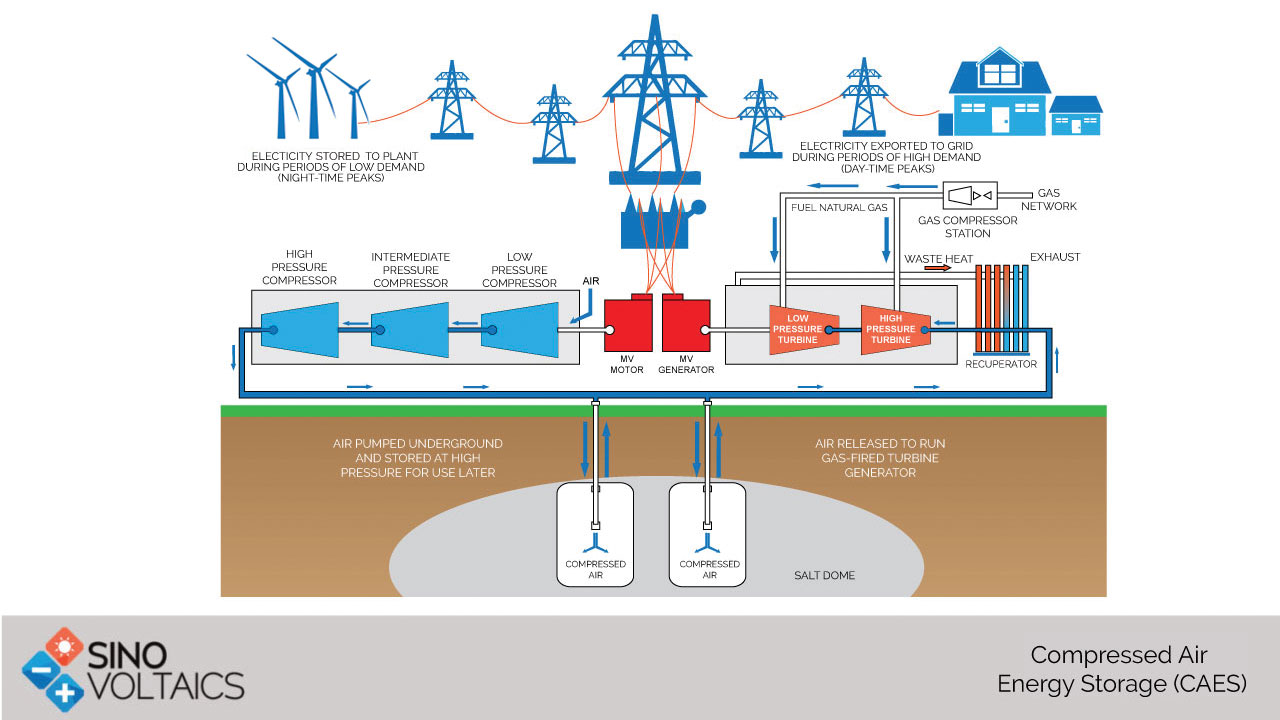
Methodology
In this technology air is taken from the atmosphere and then compressed using compressors. Air is later stored in the form of pressurized air. And when energy is required during peak periods of usage of electricity, the air is put into a combustor in a gas turbine to generate electricity.
Compressed Air storage - Advantages
- It provides solution to renewable energy intermittency
The aim of CAES like most energy storage technologies (e.g. batteries, hydrogen cells etc.) is to provide a means by which intermittent renewable energy can be combined with fossil fuel plants for meeting the demands of electricity. Due to the fluctuating and random nature of renewable energies their integration into power grid imposes many technical challenges .In this context energy storage technologies like compressed air storage help to balance the electrical load profile, thus adding flexibility on system operation and helping to incorporate the renewable sources of energy. In the past CAES technique was used to provide the grid with ancillary services. But in recent times the technology is being used as a storage solution for storing renewable sources of energy like wind and solar. For both these sources their outputs are first converted into high pressure that can be channelized and stored properly in tanks for later use.
- Advantage over battery storage systems
CAES has an advantage over battery chemistries, as there’s no degradation of capacity over time. Once the system is built, it will continue to store that quantity of energy for many years. Hence it is a good alternative to batteries.
Compressed storage: Key Issues
It’s not a standalone technology
CAES technology encompasses compression and expansion machinery, heat exchangers, the design of air stores and the design of thermal stores. It requires skillful and good engineering to set up the storage system right .A typical system arrangement is shown below (Fig.1) Geographic restrictions -Finding a storage cavern is hard CAES has some geographic restrictions, which is a big con. In addition, it is hard to locate an underground cavern structure to use as reservoir for compressed air. Cost is an issue CAES is known to be cheaper than pumped hydro storage systems; regardless they are still costly infrastructure projects in the $100-million and up bracket.
