Solar Panel Angle: how to calculate solar panel tilt angle?
Discover how to calculate the optimal solar panel angle for your solar system according to your location and the season. Two calculation methods explained.
How to calculate the Solar Panel Angle of your solar system?
The solar panel angle of your solar system is different depending on which part of the world you are. Solar panels give the highest energy output when they are directly facing the sun. The sun moves across the sky and will be low or high depending on the time of the day and the season. For that reason the ideal angle is never fixed. To get the most sun reaching the panel throughout the day, you need to determine what direction the panels should face and calculate an optimal tilt angle. This will depend on:
- Where you live
- What time of the year you need the most solar energy
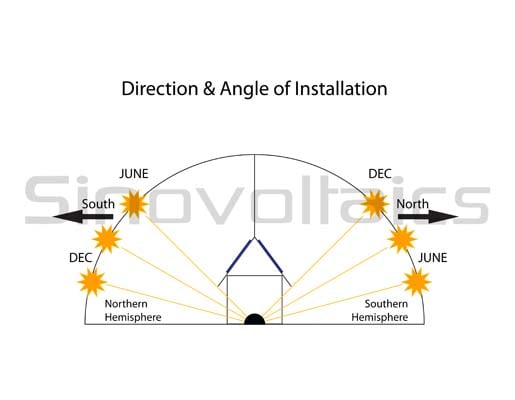
Calculating the Optimal solar panel Angle
As a rule of thumb, solar panels should be more vertical during winter to gain most of the low winter sun, and more tilted during summer to maximize the output. Here are two simple methods for calculating approximate solar panel angle according to your latitude.
Calculation method one
The optimum tilt angle is calculated by adding 15 degrees to your latitude during winter, and subtracting 15 degrees from your latitude during summer. For instance, if your latitude is 34°, the optimum tilt angle for your solar panels during winter will be 34 + 15 = 49°. The summer optimum tilt angle on the other hand will be 34 – 15 = 19°.
Calculation method two
This is an improvement of the general method that gives better results. In this method, the optimum tilt angle for solar panels during winter is calculated by multiplying the latitude by 0.9 and then adding 29°. In the above case example of a latitude of 34°, the tilt angle will be (34 * 0.9) + 29 = 59.6°. This angle is 10° steeper than in the general method but very effective at tapping the midday sun which is the hottest in the short winter days. For summer, the tilt angle is calculated by multiplying the latitude by 0.9 and subtracting 23.5°. In the above case example, this angle would be (34 * 0.9) – 23.5 = 7.1°. For optimum tilt angles during spring and fall, 2.5° is subtracted from the latitude.
Ready to maximize your solar investment?
Partner with Sinovoltaics for unmatched transparency in solar module sourcing, quality assurance, and compliance, ensuring your PV systems deliver reliable performance from day one.

Dhruva Paudel
on 03 Apr 2024Wilna Vosloo
on 24 Jul 2023James Dow
on 20 Jul 2023David
on 20 Oct 2022Aca Ceait
on 15 Jan 2023Chris
on 22 Jun 2023Asa Ceait
on 15 Jan 2023YUBA RAJ ADHIKARI
on 23 Jan 2022Mike a2zidx.com
on 16 Nov 2021Dr Abbas Ali
on 02 Nov 2021Kevin
on 13 Oct 2021Tigabu Mekonnen Belay
on 06 Oct 2021VIKASh
on 25 Sep 2021Launcelyn
on 28 Mar 2021Engr Shahzad Aslam
on 06 Mar 2021Robin hood
on 17 Feb 2021Ken A.
on 09 Nov 2020Harilal Bhatti
on 24 May 2016Raman Patel
on 26 Dec 2017Amarnath.P
on 12 Mar 2018FIROSUDHEEN
on 13 Jul 2021ishaq
on 09 Jun 2019Maxim
on 14 Dec 2016alex r. reonal
on 05 Oct 2017ramkripal
on 30 Dec 2016alex r. reonal
on 05 Oct 2017DJ
on 30 Jun 2018tabaray alam badhusha
on 14 Nov 2018Vietky
on 05 Mar 2017opeyemi gbogi
on 03 Apr 2017hasen
on 29 Apr 2017nisar samad
on 03 Jul 2017alex r. reonal
on 05 Oct 2017arun
on 27 Sep 2017Kevin
on 06 Dec 2017Vijay Ganesh
on 13 Dec 2017C.SHUNMUGHASUNDARAM Shanlee
on 08 Aug 2018Pieter
on 01 Sep 2018tabaray alam badhusha
on 14 Nov 2018Alwielland Bello
on 08 May 2019ramu
on 26 Jun 2019ATUL SHAH
on 02 Jul 2019Jon
on 22 Aug 2019Eva
on 25 Sep 2019Dave S
on 20 Apr 2022korosh
on 09 May 2020Black_whale
on 12 Jul 2020Bruce Domer
on 27 Jul 2020Mikael Palmkvist
on 31 Dec 2021Felix
on 30 Apr 2021shaharyar
on 25 Dec 2020ras
on 16 Nov 2020david aponte
on 15 Oct 2020Brian Shingleton
on 08 Oct 2020Brett
on 08 Oct 2020