Lithium-ion battery safety Concerns
How would you feel if you knew the cellphone in your pocket could burst automatically? Or that the luggage in the boot of your car carries a bottle of petrol? Or that the aircraft in which you are flying is also carrying combustible material in the luggage compartment?
Lithium-Ion (Li) batteries are most likely the future of battery power storage for some time to come. They are useful in many respects and show further promise. Batteries with lithium metal anodes offer twice as much energy density as those lithium-ion batteries using graphite (carbon) anode. They are already universal and getting more popular in all designs of equipment.
However, specific unfortunate incidents brought the spotlight on their safety. The first concern about their safety was raised when an electric vehicle using lithium batteries caught fire after striking with another car in China. It was later found that the lithium batteries were not responsible for the breakout of fire, but (about 25 % of them on the vehicle) themselves caught fire caused by a short-circuit of high voltage lines. However, the US post office did ban parcels carrying lithium batteries because of the possibility of catching fire.
Two separate battery problems in Boeing 787 Dreamliner in 2013 prompted a grounding of the complete fleet of the Dreamliner. In one of these a battery in a 787 aircraft at Logan International Airport, Boston, Massachusetts, USA, caused a fire that was traced down to a lithium-ion battery supporting onboard power system.
In 2016 came the famous case of the battery fire of the original Samsung Galaxy Note Seven. Although thorough investigations into the fire incidents did not link the incidents to battery chemistry, the battery incidents brought attention once again on lithium-ion batteries. Unfortunately, the replacement battery designed in a hurry also failed, and that was the last nail in the coffin the Note 7.
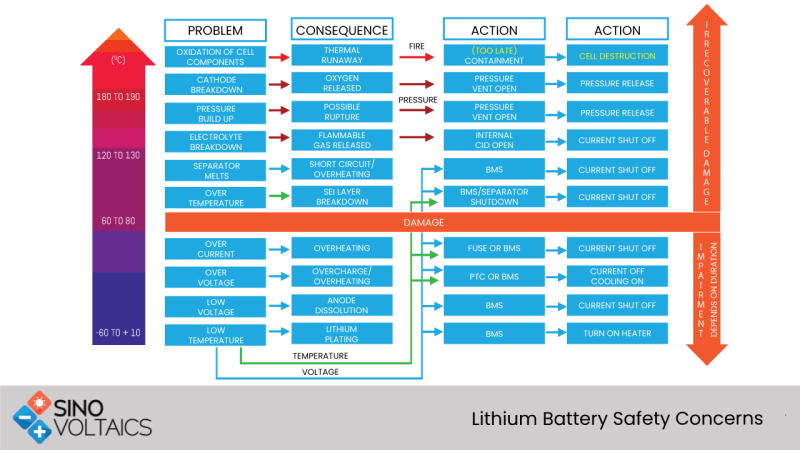
This series of safety events in a technically and commercially popular and promising battery-one deemed to be the battery of the future- raised the alarm. Lithium-ion batteries are attracting intense research and development activity aimed at safety assurance as well as performance and cost optimization.
This stress on safety is justified, because the battery is used in various devices, starting from things smaller than the cellphone to extensive battery back-ups and for massive alternate energy storage systems. Left unsafe, it can cause loss of life and property.
