LFP battery
LFP batteries: properties and usage
LFP batteries stands for Lithium iron phosphate(LiFePO4) batteries, which is known as li-phosphate batteries as well. They use phosphate as cathode material. In addition, they benefit from the low resistance properties that enhance their thermal stability and safety.
Lithium-ion batteries and concept
The most popular technology of the battery sector currently is of the lithium ion battery. Relative to other types of batteries, lithium ion batteries have better energy, power density and higher cycling ability. These qualities are extremely important in the use in modern applications like electrical and hybrid vehicles and most importantly energy storage systems as in renewable energy applications. The lithium ion batteries chemistry is the same across the different lithium-ion battery types; during discharge, Lithium-ions move to the positive cathode from the negative anode through the organic electrolyte. The anodes in all various technologies of lithium ion are all made from graphite. The differences are the cathode which contains changing cobalt, nickel or manganese concentrations. All various cathode types allow high lithium insertion and intercalation levels which result in large energy storage quantities.
LFP batteries technology and applications
LFP (Lithium iron phosphate) was invented in the year 1996. Its anode material is LiaC6, the cathode material is LibFePO4 and the carrier is Li+. They use LFP batteries in different applications like electric cars, electric buses and electric trucks. The LFP is ideal for use in electric trucks or buses – as volume or weight isn’t really a restriction as is in cars- because the battery is less energy dense yet cheaper to manufacture than other Li-ion batteries types. In addition, they use LFP batteries in other applications like electric motorcycles which need a longer life cycle and increased safety. LFP provides good electrochemical performance with lower resistance. This is enabled by the nano scale phosphate cathode material. The main benefits are long cycle life, higher current rating and thermal stability which means extra safety.
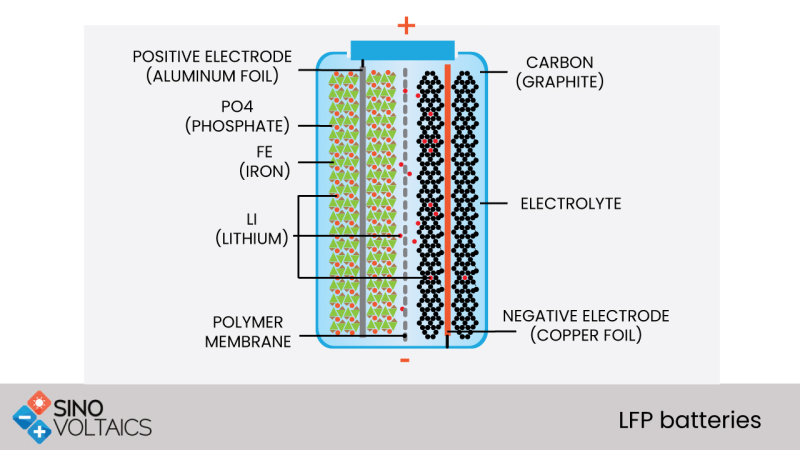 LFP batteries
LFP batteries
Advantages and disadvantages of LFP batteries
The main advantages of the LFP batteries are:
- Durability
- Long lifecycle
- Low cost
- Excellent safety
The main disadvantages of the LFP batteries are:
- More tolerant to conditions of full charge and is less stressed at higher voltage for a long time.
- lower nominal voltage which reduces the specific energy
- Higher self discharge than other types Li-ion batteries, which causes balancing issues with aging

Kenneth Evans
on 24 Apr 2021joel menkes
on 20 Oct 2021joel menkes
on 20 Oct 2021